Safety and Security Initiatives
Basic Policy
From raw material procurement to food service at restaurants, the Group is taking various measures to ensure food safety and security. At our factories, in order to ensure food safety and security, we are striving to prevent accidents and thoroughly manage safety. Specifically, from the procurement of raw materials to shipping to restaurants, we perform various inspections and checks, as well as quality and hygiene management, using the eyes of many people and specialized equipment. From the production and procurement of ingredients through to serving customers at our restaurants, we process food under strict hygiene control, and conduct stringent safety checks using both machines and people to maintain safety from the perspectives of quality and hygiene. Moreover, we perform a variety of inspections and checks at our restaurants across the country to make sure our customers can enjoy their meals with peace of mind. All employees are conscious of food safety. From cooking to ingredient management, we perform comprehensive hygiene management in compliance with our manual.
ISO 22000 Certification Received
In October 2016, the Product Department of the Group Product Division, Tokyo Factory, and Kyoto Factory of Yoshinoya Holdings became ISO 22000 certified.
ISO 22000 is an international standard for food safety management systems to ensure provision of safe food products to consumers based on the food sanitation control system of HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point). Making a Group-wide effort to ensure safe and secure products backed by international standards, we are resolved to deliver products that meet customers' expectations.
Examples of Activities
Secure Safe Beef
To ensure we always provide safe products to our customers, from raw material procurement to the provision of products at restaurants, the Group fully comprehends food safety and has numerous organizations and teams that support safety in multiple layers to continuously provide beef our customers can rely on. The American beef mainly used for Yoshinoya beef bowls strictly adheres to the international, U.S., and Japanese standards, thus ensuring safety and security.
We repeatedly check the quality of our products at local processing plants under the USDA supervision
When cattle are delivered to a processing plant, veterinarians of the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) conduct a strict checking process that includes visual inspection of the cattle as well as quarantine and disposal of cattle with a symptom of a disease. The USDA's inspectors inspect carcasses, offal, and removal of specified risk materials (SRMs). During the processing at a plant, we wash the tools for dividing carcasses with hot water per a head of cattle. Carcasses produced are then cleaned several times by means of steam pasteurization and organic acid rinses (using acetic acid and lactic acid) for sterilization. The U.S. allows a processing plant to operate only after the USDA's inspectors have confirmed that the plant appropriately performs all of the processes. So the USDA's inspectors are stationed permanently at plants to ensure stringent quality control.
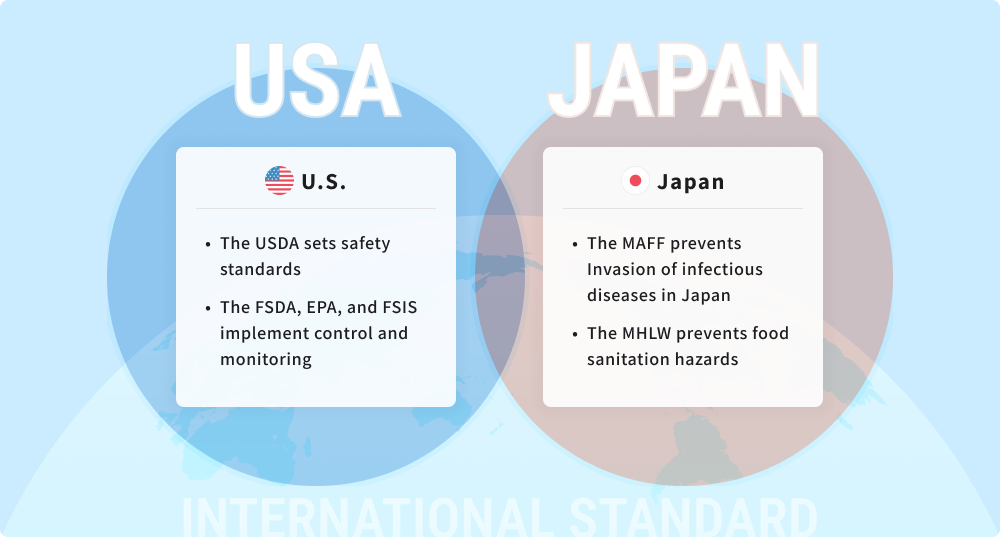
The Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries and the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare collaborate and inspect imports to Japan
Japan sets strict import standards as well. The Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (MAFF) is primarily responsible for preventing invasion of infectious diseases in Japan, and the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) is mainly in charge of preventing sanitation hazards. The two ministries collaborate to implement the control. Specifically, the Animal Quarantine Service of the MAFF inspects imported livestock products to prevent infectious diseases from infecting domestic animals via livestock products from overseas, based on the Act on Domestic Animal Infectious Diseases Control. In the case of an outbreak of an infectious disease in a foreign country, the authority would temporarily suspend imports and exports of livestock products.
Once the food has undergone inspections by the Animal Quarantine Service, a food import notification must be submitted to a quarantine service of the MHLW according to the Food Sanitation Act. Then the imported items go through a judging process where food sanitation inspectors review them and determine whether the items require a further inspection. This process is aimed at preventing sanitation hazards that result from eating or drinking the items.
Assuring safety according to the U.S. and Japanese standards, which are based on the international standards
Yoshinoya employees visit a plant to check and audit fodder and plant systems
We at the Yoshinoya Holdings Group only source beef that satisfies all of the international, U.S. and Japanese standards to serve it to customers. In addition, our employees visit a plant to check and audit whether the beef is safe, while also building relationships with meat packers The reason is that we believe that the best way to pursue both safety and security and economic rationality is to be proactive.
As for traceability, each freight exported to Japan comes with a health certificate issued by the USDA, which enables information sharing among relevant governmental organizations. This helps swiftly track and identify the item if any problem arises, ensuring the safety of beef. When our employees visit sites, they check feed and confirm factory systems. When we visit the sites, we also check the safety framework by ourselves, including the feedstuff used at farms and checking of plant systems. Assuring safety also involves Japanese units of meat packers and trading companies specialized in beef imports. Through the exchange of information with all parties in the industry, we dedicate ourselves to stable sourcing of safe beef that consumers in Japan can buy with no worries.
We carry out multiple checking procedures before beef arrives at plants for thorough safety management
The Yoshinoya Holdings Group sources the American beef based on a framework consisting of multiple safety control systems in collaboration with relevant governmental organizations and partner companies. Here is the brief summary of the processes: Firstly, the USDA's veterinarians inspect the cattle delivered to a meat packing plant from producers (contracted farmers) to determine whether they are healthy. Secondly, the USDA's inspectors inspect carcasses, offal, and removal of SRMs as well as hygiene conditions at the plant. This is the second checking process. The safety control framework incorporates a hygiene test at meat packer's lab, which represents the third checking process. Although the lab inspection takes place for each lot because of too much beef, all of its exports to Japan have health certificates by freight.
Additional stringent checking processes take place when the American beef arrives in Japan. The Animal Quarantine Service inspects the freight by actually opening the packages in the freight to check if they match the content described in a document. Then, the Animal Quarantine Service and the quarantine service of the MHLW review food import notifications and inspect the imported items, as seen above. These represent the fourth checking process.
Employees visually inspect each carcass at the plant
After temporary storage in cold storage, beef that has been checked four times goes to the Yoshinoya Holdings Group's plant. Qualified employees open all the packages and check the quality of the beef. Then we manage the production system and supply the beef to Yoshinoya stores at the plant, based on our unique Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) Comprehensive Hygiene Management System that meets the Yoshinoya Production Standards. This is the fifth checking process. Moreover, this checking process includes a series of more detailed inspections: We check the volume of fat and the quality when slicing the beef. We also remove excessive muscle and fat on the beef manually. This trimming process serves as a checking procedure of the beef too and allows our employees to check the color, smell, and other conditions of each carcass to only select beef that satisfies Yoshinoya's quality standards.
Never overlooking a problem requires us to think, “The beef may suffer from a problem somewhere." You can imagine that something bad might occur during transportation, even if the processes in the U.S. took place perfectly. Nothing is absolute in the world, and so we inevitably need to have a system in place that can detect any problem quickly. Last but not least, employees at each Yoshinoya store make sure to visually check the conditions of the beef.
Multiple checking processes from delivery of cattle to delivery of beef to Yoshinoya's plant
1st
When delivering cattle to a processing plant from a producer (contracted farmer) in the U.S.
The USDA's veterinarians conduct a checking process that includes visual inspection of the cattle as well as quarantine and disposal of cattle with a symptom of a disease.
2nd
At a meat packing plant in the U.S.
The USDA's inspectors inspect carcasses, offal, and removal of SRMs.
3rd
At a meat packing plant in the U.S.
The plant conducts a hygiene test at a lab installed in the plant.
4th
When importing the beef to Japan
Following the import quarantine inspection by the Animal Quarantine Service of the MAFF, a food import notification is submitted to the quarantine service of the MHLW, and food sanitation inspectors review the imported freight and determine whether it requires a further inspection.
5th
At Yoshinoya Holdings Group's plant
Employees open all the packages and check the quality of the beef.
We manage the production system and supply the beef to Yoshinoya stores at the plant, based on our unique Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) Comprehensive Hygiene Management System.
Secure Safe Rice
Rice is Japan's principal crop. In order to assure its safety, stringent inspection is performed pursuant to the law. Specifically, use of pesticides and fertilizers is checked; residue tests of pesticides, cadmium, and other substances are performed; and cultivation records are retained. Moreover, based on the Rice Traceability Act, Yoshinoya Holdings has a system in place for speedy tracing of test records and transaction records of all the rice received at its warehouses.
For the rice supplied to each Yoshinoya store, traceable information includes where the rice was harvested, the variety, and the grade, as well as the production lot at the rice polishing plant and the grower's inspection records. In the event of any quality problem, the distribution route in question can be identified swiftly to find causes and deal with the problem.
About the Rice Traceability Act

At each process in the distribution of rice and processed foods containing rice, it is mandatory under the act to prepare and retain transaction records and provide the information on where the rice was harvested.
Checks of quality management systems of rice polishing plants
For brown rice that has passed inspection, there is still a risk of contamination by foreign matter, such as stones and insects. We use high-precision sorters in the process for removal of foreign matter. Having set quality standards greatly exceeding the typical standards in the rice industry, we have realized virtually 100% removal of foreign matter. Moreover, we conduct periodic audits of rice polishing plants nationwide in order to prevent any quality management failure due to human error and we are also emphasizing provision of on-site guidance, including thorough acceptance inspection of ingredients.
Thorough quality management at each store
No shelf lives are determined for rice by law or regulation. However, from the viewpoint of freshness control, at Yoshinoya Holdings the time from rice polishing to delivery to stores is set to be within 10 days and our stores are required to use the rice within 30 days. In practice, rice is not stocked at stores for extended periods because of daily delivery of the necessary quantities of ingredients ordered by stores. Area managers always focus on the status of quality management and hygiene management performed by store staff. In addition, mindful of the risk of rice becoming wet or containers being damaged during storage, we continuously review the strength of rice containers and the locations of ventilation holes.
Quality management of beef bowl overseas based on the Standards of Principal Ingredients
In overseas business development, the Yoshinoya Holdings Group has been implementing quality management overseas based on the Standards of Principal Ingredients that strictly specify the taste of Yoshinoya beef bowl. Quality management in accordance with the specifications ensures minimal variation in the taste of Yoshinoya beef bowl even though ingredients other than beef and sauce are procured, in principle, at the discretion of regional headquarters and franchises. Regarding rice, in accordance with the quality standards specified by the Standards of Principal Ingredients, rice produced in a country where Yoshinoya stores operate is blended so as to be the optimum for beef bowl. Yoshinoya stores in China use rice grown in China and those in the U.S. use rice grown in the U.S.
However, in view of the food culture and consumers' preferences in each area, maintaining quality based on the common standards is not a straightforward matter. Therefore, we have put in place a system whereby personnel in charge of merchandising and personnel in charge of quality management in each country can consult Yoshinoya Holdings buyers who have a sure grasp of the essence of the taste of Yoshinoya's beef bowl. Personnel in charge of quality management and field counselors in each area periodically audit stores' management systems and ingredient suppliers, providing guidance to them so as to ensure customers can enjoy Yoshinoya beef bowl of uniform quality anywhere in the world.
Hanamaru Udon Quality Control
Hanamaru has been maintaining consistent quality control and safety management—encompassing everything from procurement of wheat flour, manufacturing, and logistics, to cooking at stores—while flexibly responding to change in line with the ongoing expansion of the business. Just like the ideal noodles pursued by Hanamaru Udon, striking a perfect balance between tenderness and firmness, Hanamaru continues to create value with delicious Sanuki-style udon.
Central kitchen system for uniform noodle production technology and consistent quality
Raw wheat received by flour millers is milled in the most optimal way to make our proprietary Hanamaru Flour, which finds its way to our noodle production plants at five locations in Japan (Hokkaido, Chiba, Shizuoka, Takamatsu, and Okinawa) under stringent quality control.
We are committed to delivering noodles to our restaurants while still fresh. Certainly, we can opt for producing noodles at each store rather than at the central kitchen system. But udon, made only from wheat flour, water, and salt, is so delicate that in order to maintain consistent quality, an artisan needs to apply his or her knowledge and techniques for adjusting the quantities of water and salt according to the air temperature and humidity on each day and for fine-tuning the temperature of dough.
Most importantly, noodle production at a plant ensures thorough safety management. Ever since our inaugural Takamatsu plant came on stream, our motto at production workplaces has been “safety, reliability, quality, and efficiency." This order of priority highlights our conviction that safety always comes first and is the precondition for achieving reliability, quality, and efficiency.
Automation achieves constant quality over the long term
Hanamaru fully automated the noodle production line at its Chiba plant in 2016. Machines execute the processes that require craftmanship but are essentially simple, with machine control reproducing the craftsmanship. As data are stored for all production processes, such as the water quantity, temperature, and the degree of kneading, craftmanship is digitized, which contributes to constant quality over the long term. The digitization also has significant impacts on the investigation in the event of trouble and the technology improvement for the future.
Advantages of having five noodle plants nationwide
Having several noodle plants nationwide not only enhances distribution efficiency but also minimizes risk as plants can complement one another in the event that operation ceases due to an emergency. Each plant has spare capacity so that plants can complement one another and deliver noodles to franchises and all other stores even in the eventuality.
The production environment, such as the climate, of each of our plants differs and they also procure wheat from different flour millers, leaving a difference in quality between production regions. In order to ensure such difference falls within a tolerable range, members of the Production Division check noodles produced at all our plants by means of sensory analysis once every two weeks. Some might wonder why we use sensory analysis, but they can notice the slightest change in taste not evident in the data because they eat Hanamaru Udon so often.
Hanamaru Udon noodle production process at the Chiba plant

Reducing food losses by order management between stores and plants
To perfect logistics from plants to stores, we have refined temperature control. Whereas food is typically refrigerated at three degrees Celsius for warehouse storage and truck delivery, we specify storage of Hanamaru Udon at five degrees Celsius. This is because condensation caused by sudden change in temperature alters the moisture content of noodles and undermines their quality. We are also continuing our efforts to eliminate the exposure of udon to room temperature during shipment.
Our management system between plants and stores involves thorough order placement/taking management, which helps to reduce food losses. Plants other than the Chiba plant must ship noodles within two days from production and dispose of any remaining noodle whose shipping deadline has expired. Therefore, the plants forecast the required quantity based on the historical record of order placement from stores and make no excess inventory. Meanwhile, stores place orders every day for noodles for the day after next and only retain surplus inventory consumed in half a day. In this way, we systematically reduce food losses to nearly zero during the process from production to storage at stores.
The made-to-order system does not ensure the stable supply at the Chiba plant, which produces the majority of Hanamaru Udon noodles. Accordingly, its production plan includes a certain surplus. To prevent food losses at the Chiba plant too, we have introduced the deaeration packaging, a novel packaging format, in the production process and successfully extended the freshness date from production to a maximum of 15 days.
Pursuing safety and quality thoroughly by temperature control and time management
For quality management at stores, in addition to the standard procedure for temperature control of refrigerators, meticulous operation is essential to prevent use of out-of-date noodles through human error. In this regard, each store is required to restock shelves in the refrigerators after the store is closed to confirm that the noodles are placed in the order of delivery. Our stores also make sure to check the use-by date of the noodles they are using every three hours.
Time management from the point in time when noodles are removed from a refrigerator and put in a pot has an important bearing on quality management at stores. Noodles are cooked for just over 10 minutes and time for rinsing them in cold water to maintain the firmness is also strictly set. Boiled udon noodles are placed on trays, boiled again when a customer places an order and then served to the customer. The time during which boiled udon noodles are left on trays is called the holding time, which is carefully managed.
Whether or not the noodles left on trays go to waste depends on the accuracy of store staff's prediction of the number of customers. Fewer customers during the holding time than predicted mean that we have no choice but dispose of the boiled udon in excess. Nevertheless, we prioritize food safety and quality management over efficiency, based on which we are implementing meticulous time management and working to predict the number of customers more accurately.
Supervisors in charge of stores are responsible for implementation of meticulous operational procedures and quality checks. Managerial personnel such as General managers and Managing Supervisors visit stores in each area, perform sensory analysis, and exchange opinions. We have put in place systems that enable us to investigate the causes if any abnormality is detected by tracing back from the logistics phase to the production processes and ultimately to the flour millers that supplied the wheat flour.
Everyone involved in Hanamaru Udon—whether members of the Production Division, staff engaged in noodle production at plants, our business partners including trading companies, flour millers, transportation companies, and store staff—is striving to enhance quality with the commitment to “offering safe and delicious udon to customers." This commitment to providing value remains unchanged in the future when we engage in a new round of store development.
Time-managed operation at stores
